Understanding Minting in the Cryptocurrency World
Every day, cryptocurrencies are processed in the millions, fueling exchanges and financial transactions across the globe. But what fuels this vast ocean of crypto? It doesn’t just materialize—there’s a distinct process involved. If you’re curious about how crypto supply grows and why some assets appreciate over time, you’ll want to dive into the world of minting. This article will unravel the concept of minting in cryptocurrencies, exploring what it entails and how it works.
What Minting Means in Crypto
Minting refers to the act of creating new digital assets on a blockchain. This encompasses both the generation of new cryptocurrency coins and the crafting of unique items like non-fungible tokens (NFTs). At its core, minting is how tokens are birthed and integrated into the cryptocurrency ecosystem, paving the way for new forms of digital ownership and transaction.
How Minting Works for Coins and Tokens
The minting process varies significantly across different types of digital assets:
-
Cryptocurrency Minting: New coins are introduced and integrated into the blockchain typically via mechanisms such as proof-of-stake (PoS). In this setup, validators help maintain network security and, as a reward, receive newly minted coins. This method establishes a steady growth in cryptocurrency supply.
-
NFT Minting: The process of minting NFTs involves converting digital files—be it art, music, or in-game items—into unique tokens on the blockchain. Some key features of minted NFTs include verifiable ownership and tradability, thanks to their distinct IDs.
- Smart Contract Minting: In certain cases, tokens get minted automatically through smart contracts. These self-executing contracts, governed by code, generate new tokens following specific actions—like participation in a game or staking assets—without the need for intermediaries.
Minting vs. Mining vs. Staking
Minting can be easily confused with mining and staking; while all are connected to the cryptocurrency arena, they serve different purposes. Here’s a simplified comparison:
| Category | Minting | Mining | Staking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Create new tokens/NFTs | Add new blocks + create coins | Secure the network + earn rewards |
| How It Works | Smart contracts or PoS create assets | Solve complex equations using computational power | Lock tokens to validate transactions |
| Energy Use | Low | Very high | Low |
| Requirements | Wallet + platform | GPUs/ASICs + high power | Tokens to stake |
| Rewards | Newly minted tokens/NFTs | Block rewards | Staking yield |
| Risks | Smart contract vulnerabilities | Hardware costs + market volatility | Slashing or loss of staked assets |
Key Features of Minting
-
Token Creation: Minting signifies the generation of new tokens or coins on a blockchain. This doesn’t involve physical items; rather, it entails adding a block that records the newly minted assets on a digital public ledger. Different consensus mechanisms, like PoS, facilitate this process through token staking.
-
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts handle the minting process in an automated fashion. By adhering to predetermined rules about the number of tokens created or their recipients, these contracts validate transactions, ensuring accuracy and transparency through decentralized ledgers.
- NFT Creation: The minting process also applies to NFTs, where digital files morph into unique blockchain assets. As these NFTs are minted, they are recorded permanently on the blockchain, assuring authenticity and offering creators a secure route for sharing their digital art.
Costs, Chain Choices, and Examples
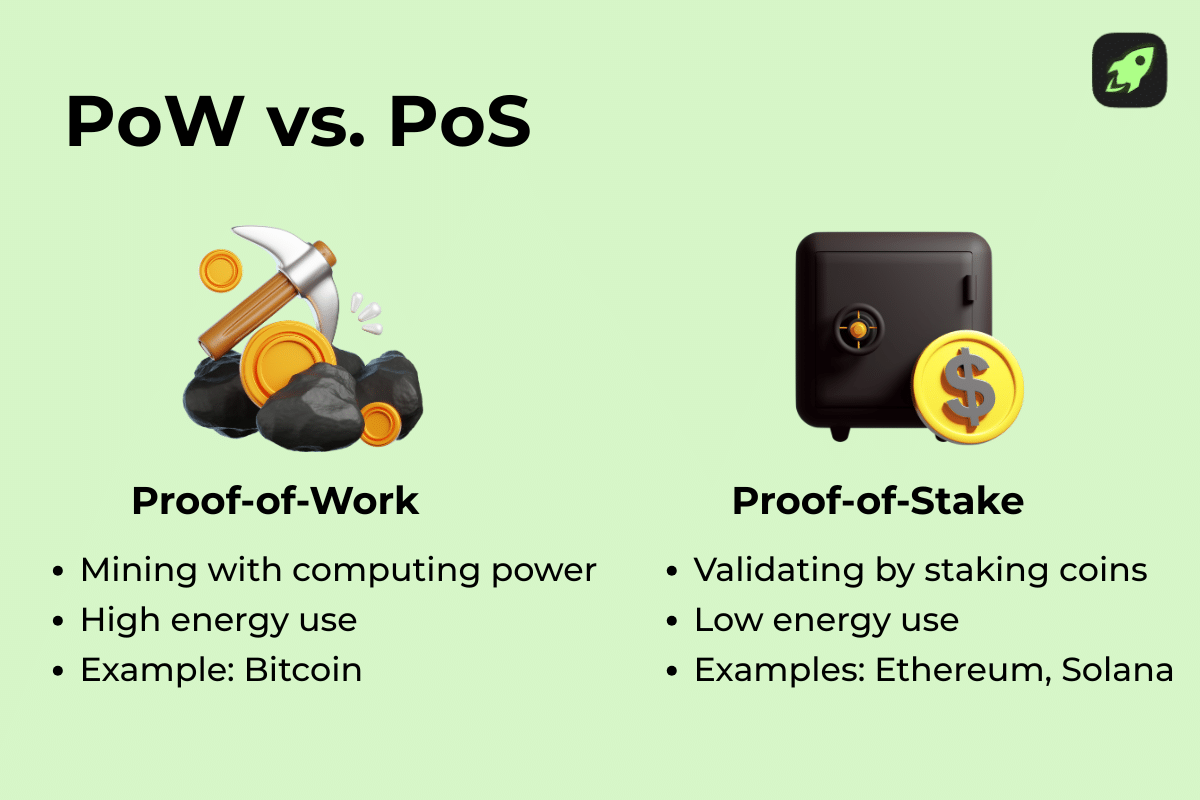
The costs of minting vary greatly depending on the blockchain and its method of validating transactions. Blockchains employing proof-of-work (PoW) can incur high minting costs due to the need for specialized hardware, computational intensity, and elevated transaction fees. Conversely, proof-of-stake (PoS) networks like Ethereum post-upgrade, Solana, and Polygon offer more environmentally friendly and cost-effective minting options that involve token staking instead of energy-intensive computing.
For instance, when minting an NFT on the Ethereum blockchain, fees can spike during peak hours. However, alternatives like Polygon or Solana present cheaper and faster options, with PoS chains generally requiring a minimal upfront investment for minting compared to PoW mining’s significant hardware costs.
Benefits of Minting
Minting cryptocurrencies or NFTs offers numerous advantages, particularly as decentralized finance (DeFi) gains traction.
-
Accessibility: Unlike crypto mining—often hindered by high demands for costly hardware—many PoS blockchains allow users to mint coins by staking tokens, enabling broader participation with lower investments.
-
Efficiency: Minting on PoS networks is a more sustainable approach compared to energy-intensive mining, consequently contributing to a greener crypto ecosystem.
- Creator Empowerment: For artists and creators, minting NFTs provides a pathway to convert digital works into blockchain assets, granting them verification and broader market reach.
Risks and Limitations
Despite the many advantages inherent in minting, beginners must understand the associated risks. Even on PoS networks, locking funds for minting can lead to penalties, resulting in a loss of staked tokens.
In contrast, PoW mining demands not only hardware and substantial energy but also entails high upfront costs. When it comes to smart contract-based minting, risks arise from potential coding errors, exorbitant transaction fees, or malevolent contracts that could result in lost assets.
A lack of adequate knowledge surrounding the blockchain, gas fees, or consensus mechanisms could also lead to overspending, inefficiencies, or unintentional losses.
Use Cases
Minting extends far beyond mere currency creation; its applications are extensive across various industries:
Digital Art and Collectibles
In the burgeoning NFT realm, minting converts digital files into blockchain assets, ensuring creators receive legitimate credit while eradicating counterfeit copies. Notably, collectors attain verified ownership of their assets, which are recorded in a publicly accessible manner on the blockchain.
Virtual Real Estate and Gaming Items
Within gaming and metaverse platforms, assets like in-game items and virtual land are minted, allowing players true ownership. Transactions are consolidated through the blockchain—facilitating verification without reliance on corporate servers—enabling fluid trading and unique digital experiences.
Music, Licensing, and Identity Assets
Musicians can tokenize songs, licenses, and certificates via minting, creating tamper-proof entries for swift validation. This not only mitigates fraud but also nurtures direct ownership and novel revenue models. Similarly, identity components can be minted to enhance security during verification processes.
Stablecoins and Token Minting
Stablecoins often arise through minting, wherein tokens are generated rapidly following collateral deposits into protocols, adhering to on-chain rules rather than traditional mining methodologies.
Understanding the various facets of minting in the cryptocurrency ecosystem is essential for anyone looking to engage meaningfully with digital assets. By being informed about the processes, opportunities, and risks, individuals can navigate this dynamic landscape with confidence and insight.



